Summary of the Blog
- What is Ethical Hacking?
- The Importance of Ethical Hacking
- Types of Hackers
- Ethical Hacking Techniques and Tools
- Legal Framework of Ethical Hacking
- The Ethical Hacking Process
- Cybersecurity Basics
- Career Paths in Ethical Hacking
- Real-Life Examples in Ethical Hacking
- Ethical Considerations in Ethical Hacking
- Learning Resources and FAQs
What is Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hacking is like being a superhero in the digital world. Unlike illegal hacking, where the hacker breaks into systems to cause harm or for personal gain, ethical hacking is used for good. It involves legally breaking into systems to find weaknesses and then fixing them to improve security. The purpose? To make the digital world a safer place for everyone.
The Importance of Ethical Hacking
In today’s world, where our lives revolve around digital platforms, ethical hacking is like a shield that protects our data and systems from cybercriminals. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding our personal and business information against malicious attacks.
- It protects data and systems in a world reliant on digital platforms.
- Safeguards personal and business information against malicious attacks.
- Detects weaknesses, prevents cyber attacks, and strengthens security.
- Builds trust and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
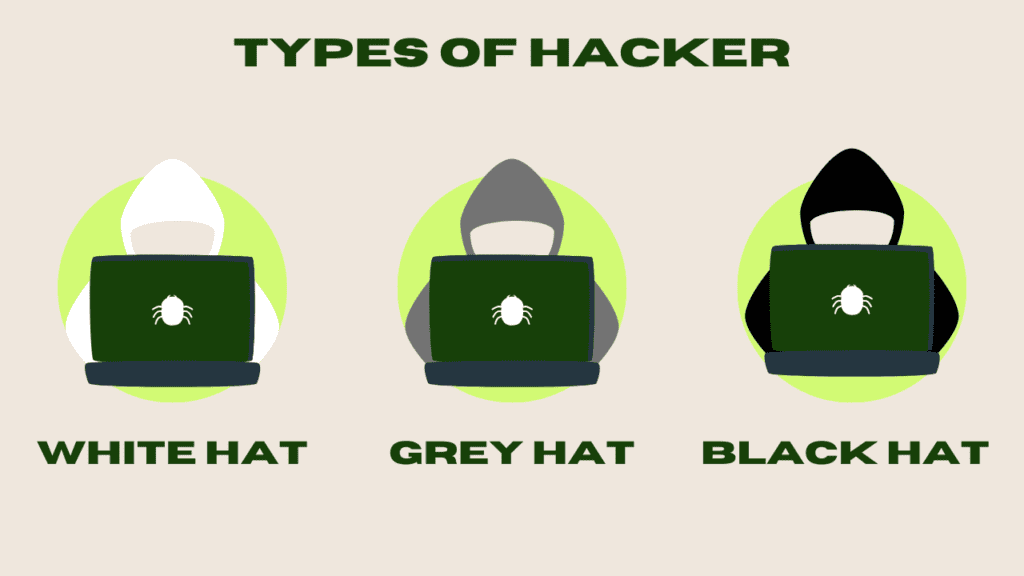
Types of Hackers
- White Hat Hackers: Ethical hackers who protect systems.
- Black Hat Hackers: Villains who engage in illegal activities.
- Grey Hat Hackers: In-between, often without malicious intent.
Ethical Hacking Techniques and Tools
Ethical hackers use a variety of tools like network scanners, vulnerability scanners, and ethical hacking software kits. They also employ techniques such as Penetration testing to assess the security of systems. These tools and techniques help them identify and fix vulnerabilities.
here are five common ethical hacking techniques and tools:
Phishing: This is a cyber-security attack where a hacker sends messages pretending to be a trusted person 1. The goal of phishing is to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other confidential data.
Sniffing: Sniffing is the process of keeping track and capturing all the packets passing through a given network 1. Ethical hackers use sniffing techniques to identify vulnerabilities in a system and improve its security 2.
Social Engineering: Social engineering is used to convince people to reveal their confidential information 1. This technique involves manipulating people into divulging sensitive information by exploiting their trust, fear, or greed.
Footprinting: Footprinting is the process of gathering information about a target system or network 1. Ethical hackers use this technique to identify potential vulnerabilities in a system and to plan their attack.
SQL Injection: SQL injection is a technique used to exploit vulnerabilities in a website’s database 1. By injecting malicious code into a website’s database, an attacker can gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.

Legal Framework of Ethical Hacking
- Ethical hacking is legal with authorization to probe systems, respecting privacy.
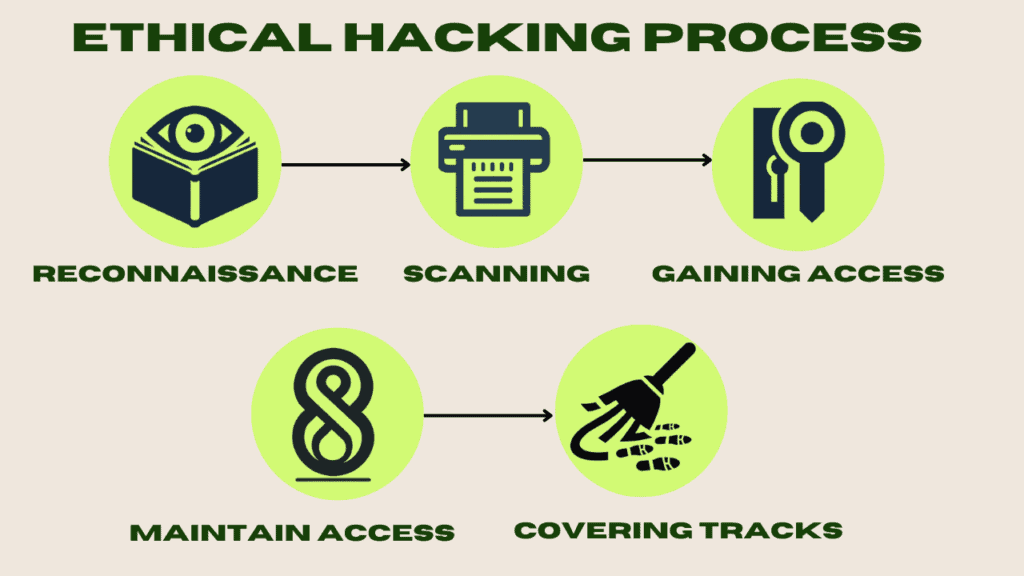
The Ethical Hacking Process
The process typically includes:
- Reconnaissance: Gathering information about the target.
- Scanning: Identifying potential vulnerabilities.
- Gaining Access: Testing the security of the system.
- Maintaining Access: Checking if the system’s defenses can be bypassed.
- Covering Tracks: Ensuring no trace is left behind.
Cybersecurity Basics
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks. It’s like a digital defense system that keeps your personal and professional information safe from cyber threats such as hacking, data breaches, and identity theft. As we rely more on the internet for daily activities, understanding and implementing good cybersecurity measures becomes essential to safeguard our digital lives.
- Protecting Information: Cybersecurity is about keeping your digital information safe from unauthorized access or theft.
- Strong Passwords: Use complex passwords with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. This is like having a strong lock on your door.
- Regular Updates: Keep your software and operating systems up to date. These updates often include fixes for security weaknesses.
- Avoiding Phishing Scams: Be cautious of suspicious emails or messages. Don’t click on unknown links or share personal information.
- Firewalls and Antivirus Software: Use firewalls and antivirus programs to block harmful intrusions and detect malware.
- Secure Networks: Use secure, encrypted networks for internet access, especially for confidential transactions. Avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities.
- Backup Data: Regularly back up important data to a secure location. This is like having a safety deposit box for your digital information.
- Educating Yourself: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and how to avoid them. Knowledge is a key defense in cybersecurity.
LEARN MORE ABOUT CYBERSECURITY >> (SEE THE NEXT PAGE FOR MORE INFORMATION)
Career Paths in Ethical Hacking
A career in ethical hacking involves safeguarding computer systems and networks by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities. It requires education in computer science or cybersecurity, certifications like CEH and CISSP, and proficiency in hacking techniques. Roles range from entry-level security analyst to senior penetration tester, with opportunities in various industries. Salaries vary based on experience, location, and specialization, but the demand for ethical hackers continues to grow as cyber threats increase.
- Security Analyst: Protecting an organization’s data.
- Penetration Tester: Testing systems for vulnerabilities.
- Security Consultant: Advising organizations on security strategies.
- Certified Ethical Hacker: Holding a specific certification that validates skills
- Information Security Manager: Managing an organization’s overall data security.
- Forensic Analyst: Investigating breaches and cybercrimes.
- Incident Responder: Addressing and mitigating the impact of security incidents.
- Security Software Developer: Creating tools for security testing.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Leading an organization’s security strategy and operations.
- Security Architect: Designing secure network and system architecture
- ALL About career paths and salary in Ethical Hacking >> (SEE THE NEXT PAGE FOR MORE INFORMATION)
Learning Resources
Books: The Basics of Hacking and Penetration Testing” by Patrick Engebretson.
Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy and Coursera offer courses in ethical hacking.
Online Website : SANSE INSTITUTE
Learn More About Ethical Hacking
- learn More about cybersecurity >>
- career path in ethical hacking >>
- what is penetration testing >>
- ethical hacking techniques and tools >>
- Advanced guidance About Ethical hacking >>
FAQs

- What is ethical hacking in simple terms?
- It’s using hacking skills to identify and fix security vulnerabilities legally.
- Is ethical hacking legal?
- Yes, when done with permission and for improving security.
- Do ethical hackers need a lot of technical knowledge to start?
- A basic understanding of IT and cybersecurity is needed, but the field is open to learners.
- What’s the first step to becoming an ethical hacker?
- Start with learning the basics of cybersecurity and consider getting certified.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ethical hacking plays a crucial role in today’s digital landscape, as it helps organizations identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems, thereby enhancing cybersecurity. Ethical hackers, also known as white hat hackers, use their skills and knowledge for the greater good, helping to protect sensitive data and prevent cyberattacks. By staying within legal and ethical boundaries, ethical hackers contribute to a safer online environment for individuals and businesses alike, highlighting the importance of their role in the ongoing battle against cyber threats.